Chinese Internet Censorship Holds Back Freedom
Earlier this month we celebrated the World Day Against Cyber Censorship. This is a rally for an unrestricted internet and a fight against governments deterring and censoring online free speech.
Amnesty International notes that China “has the largest recorded number of imprisoned journalists and cyber-dissidents in the world“. They remain the leading example of the problems cyber censorship creates. The government blocks many websites, searches, and software based on content alone. Now a new rule could make Chinese Internet censorship even more restrictive for its citizens.
Search Word Blocking
China blocks searches that involve a negative take on the government, sociopolitical matters, etc. You may get a “page cannot be displayed” error or a very skewed version of the results – see below for examples
Examples of search words that will give users a “page cannot be displayed”
 Persecution
Persecution- Tibetan Independence
- Tienanmen Square
- Democracy Movements
- Oriental Red Space Time (code for an anti-censorship video)
Website Blocking
China blocks many sites simply because of their content. They block all social media except for Chinese based social media sites because of the difficulty they have complying with censorship rules. Although recently, Mark Zuckerberg has still been trying to get Facebook in China. Google also tried to make a censored version of its search engine for China but was repeatedly banned and eventually gave up.
Examples of sites that are currently blocked in China
 Google (Which includes YouTube and Gmail)
Google (Which includes YouTube and Gmail)- New York Times
- Dropbox
Microsoft’s Windows 10
Microsoft recently created a version of Windows 10 to fit the strict rules of censorship in China. They partnered with a state-run technology and defense company, CETC. Microsoft is not giving very much information away about how they have changed their product to make it comply, only that it doesn’t have the same apps, services, or additional device management and security controls.
The Internet Domain Name Management Rules
 Just when you think China’s Internet censorship cannot get more strict, its government announced on March 28th that websites will be more strictly managed within China under the draft Internet Domain Name Management Rules. The new rules would make sites register domain names with local service providers and with the authorities.
Just when you think China’s Internet censorship cannot get more strict, its government announced on March 28th that websites will be more strictly managed within China under the draft Internet Domain Name Management Rules. The new rules would make sites register domain names with local service providers and with the authorities.
It is not clear whether this is going to apply to all websites or just those that Chinese servers host. As of right now, the rule is only a draft and will be going to the Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology on April 25th, which will then determine if this affects websites globally or locally.
 If this does apply to all websites then the global Internet might die at China’s border. Many domains would not make it by the new rules and authorities would block much of the content.
If this does apply to all websites then the global Internet might die at China’s border. Many domains would not make it by the new rules and authorities would block much of the content.
 If this only applies locally this would make it much more convenient for the Chinese government to censor websites.
If this only applies locally this would make it much more convenient for the Chinese government to censor websites.
To explain how restrictive the rule would be, Article 28 lists out what is not allowed to be in a domain name. Here are just a few of the stipulations:
- jeopardize national security, leaking state secrets, subverting state power, undermining national unity;
- incitement to ethnic hatred, ethnic discrimination, undermining national unity;
- spreading obscenity, pornography, gambling, violence, homicide, terror or instigate crimes;
- insult or slander others, infringe upon the legitimate rights of others;
US Search Engine vs The ‘Great Firewall’ Search Engine
You can surf the web comparing Google in the US and the comparative Baidu in China to see the difference in censorship. The traveling pop-up Firewall Internet Cafe even sets up computers specifically so its customers can experience China’s great firewall firsthand. Different results show up depending on the topic.
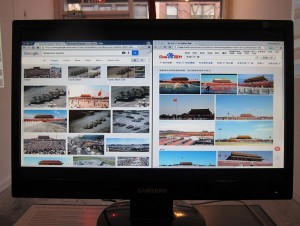
Photo Source hyperallergic.com
Example: Tiananmen Square
“Google pulls up the famous image of the “tank man,” among other photographs related to the June 4, 1989 massacre; Baidu, however, finds scenic snapshots of the city square. The browser also posts a line above the results that notifies users of the sensitivity of their search subject.”
How America Fights to Keep the Internet Open and Free
Net Neutrality
In America we have an open internet through Net Neutrality from the FCC. This means that we all have the right to communicate freely online, protecting our first amendment of Freedom of Speech. This also means that no internet provider can block, throttle, or discriminate against any applications or content on their networks.
Some things China has done such as blocking websites completely and filtering out results from searches, are examples of why we have Net Neutrality. This does not mean that we should take Net Neutrality for granted. In fact, it has so far withstood a barrage of attacks, specifically from Congress and cable/phone companies (Such as Comcast and Verizon).
To help Save the Internet, visit Free Press.
Proposed Acts in the US that Promote Online Censorship
Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA)
This act would expand US law enforcement to stop copyright infringement but many worry that this promotes censorship.
PROTECT IP Act (PIPA)
The Preventing Real Online Threats to Economic Creativity and Theft of Intellectual Property Act, or PIPA, was a proposed law to give governments and copyright holders tools to curb access to “rogue websites dedicated to the sale of infringing or counterfeit goods”. This road leads directly to a censored Internet.
EU-US Privacy Shield Still Not Protecting Your Privacy
EU-US Privacy Shield Still Not Protecting Your Privacy
Full text of the new draft EU-US Privacy Shield was released February 29th but has not been signed yet. They have made some changes from the previous Safe Harbor Agreement. While some are good improvements, some seem to have not changed how our data is handled at all. A conclusion on if the draft agreement will be acceptable should be made by mid-April to the end of April.
History: Safe Harbor Agreement
Before going in to the Privacy Shield here is the history of why we needed a new agreement between the European Union and United States. In an earlier blog, Safe Harbor Ruled Invalid, How it Affects You, we talked about the invalid ruling of the Safe Harbor Agreement and how it affected businesses and consumers. So here’s a little history on the old Safe Harbor Agreement:
The European Union (EU) and the United States (US) established the Safe Harbor Pact in 2000. This allowed businesses to legally funnel info across the Atlantic. Common data storage and transfers might include global commerce, sending and receiving emails, and even posting on social media. US companies can “self-certify” that they meet the stricter European privacy standards.
In early October of 2015, the European Court of Justice found the US approach to domestic surveillance and absence of legislation governing certain privacy rights was not up to European standards following a case brought by an Austrian student Max Schrems. The EU then made the Safe Harbor pact invalid. They believe the US has compromised their data and would like for some changes to happen to ensure the US is not spying on their citizens.
What’s New
 While there are some improvements to the Trans-Atlantic data transfer deal many say it does not differ much from the original Safe Harbor and does not address the “core concerns and fundamental flaws of US surveillance law and the lack of privacy protections under US law.”
While there are some improvements to the Trans-Atlantic data transfer deal many say it does not differ much from the original Safe Harbor and does not address the “core concerns and fundamental flaws of US surveillance law and the lack of privacy protections under US law.”
Key Positive Takeaways:
[space10]Citizen and Company Complaints
 The new agreement gives companies and citizens the chance to complain and dispute any mishandling of records and personal information. Governments must resolve such complaints within 45 days or use a free “alternative Dispute Resolution”.
The new agreement gives companies and citizens the chance to complain and dispute any mishandling of records and personal information. Governments must resolve such complaints within 45 days or use a free “alternative Dispute Resolution”.
Ombudsman
An ombudsman is a public advocate representing the interests of the public by investigating and addressing complaints. An ombudsman within the US State Department will handle any allegations of privacy violations.
Key Negative Takeaways:
[space10]Collecting Data in “Bulk”
In a Press Release from February 29th the European Commission states there will be “no indiscriminate or mass surveillance by national security authorities.” But then is contradicted by this:
6 exceptions where US can collect data “in bulk”:
- Detecting and countering certain activities of foreign powers
- Counterterrorism
- Counter-Proliferation
- Cybersecurity
- Detecting and countering threats to US or allied armed forces
- Combating transnational criminal threats, including sanctions evasion
US Judicial Redress Act
 In addition to the Privacy shield, President Obama signed the U.S. Judicial Redress Act on February 24th that will “give EU citizens access to US courts to enforce privacy rights in relation to personal data transferred to the U.S. for law enforcement purposes. ” […] The Judicial Redress Act will extend the rights U.S. citizens, and residents enjoy under the 1974 Privacy Act also to EU citizens.”
In addition to the Privacy shield, President Obama signed the U.S. Judicial Redress Act on February 24th that will “give EU citizens access to US courts to enforce privacy rights in relation to personal data transferred to the U.S. for law enforcement purposes. ” […] The Judicial Redress Act will extend the rights U.S. citizens, and residents enjoy under the 1974 Privacy Act also to EU citizens.”
At first that sounds good. After further research on the Privacy Act of 1974, many believe that the Privacy Act is “worthless”, with similar views from the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF),. There are many exceptions including 32 CFR 322.7 which exempts the NSA from rules of privacy on records maintained on individuals, according to 5 U.S. Code § 552a.
“Essential Equivalence” Non-Existent
 One of the most important parts of changing this agreement was to have “essential equivalence” of European data protection in the US. Max Schrems points out that this deal falls short:
One of the most important parts of changing this agreement was to have “essential equivalence” of European data protection in the US. Max Schrems points out that this deal falls short:
“The new deal does not even address the matter of private sector data misuse, despite the fact that there would have been much more leeway than in the government sector. There are tiny improvements, but the core rules on private data usage are miles away for EU law.”(TechCrunch)
 Privacy Shield Certified
Privacy Shield Certified
Under the Privacy Shield a business can become ‘certified’ to establish “adequate” protections for Trans-Atlantic data transfers. While this helps to protect your business from data transfer problems, it does not protect you completely.
The new agreement allows Data Protection Authorities (DPAs) to suspend data flow regardless of a business being Privacy Shield Certified. This would mean you cannot secure continuous data flow for your company.
The Outlook
 The EU-US Privacy Shield still needs to be approved by the EU’s WP29, also known as the Article 29 Working Party, and from the privacy issues others have already found in the draft it does not seem likely it will be approved.
The EU-US Privacy Shield still needs to be approved by the EU’s WP29, also known as the Article 29 Working Party, and from the privacy issues others have already found in the draft it does not seem likely it will be approved.
“They tried to put 10 layers of lipstick on a pig, but I doubt the court and the DPA’s now suddenly want to cuddle with it”
-Max Schrems
NSA Surveillance and Online Privacy
Who are the NSA?
The National Security Agency (NSA) is a powerful United States intelligence organization. Basically, they are responsible for collecting, processing, and monitoring global data for intelligence purposes. The NSA has a stated role to advance national security while protecting the freedoms, civil liberties, and privacy rights guaranteed by the Constitution and federal law.
What is the issue?
Many studies, cases, and documents show that the US government is spying on American citizens using online NSA surveillance. As Americans, this invades our Freedom of Speech and our Right to Privacy. The ACLU has called this activity “unconstitutional surveillance of Americans’ communications”.
Some Examples
An internal NSA audit from 2012 revealed they committed 2,776 incidents of unauthorized surveillance of Americans or foreign targets in the US over a one-year period.

On May 20, 2013, Edward Snowden released files from the NSA which described, as he put it, “systematic surveillance of innocent citizens.” Based on Snowden’s documents, the NSA has at least nine major tech companies gathering data on selected surveillance targets. This revelation caused online privacy concerns to increase dramatically in the US.
Then on Dec 24, 2014, a Freedom of Information lawsuit filed by the ACLU revealed NSA documents from 2001 to 2013. Overall, these documents showed that there were instances of unauthorized surveillance of US organizations, spouses or love interests, and more American citizens.
What is a Digital Pat Down?
The inner workings of an intelligence machine like the NSA can be difficult to grasp. From leaked documents so far, we can surmise that the NSA is performing secret “digital pat downs” on American citizens somewhat regularly. This happens without our knowledge or consent.
First, an NSA analyst identifies a target and submits a request to the FBI’s Data Intercept Technology Unit. Next, dedicated employees at various tech companies receive the request and gather the requisite data. This may include emails, chat logs, and videos. Once the data is compiled, it is sent back to the FBI for analysis.
The National Security Agency is also piggybacking on the tools that enable Internet advertisers to track consumers, using “cookies” and location data to pinpoint targets for government hacking and to bolster surveillance. We’ve talked in detail about mobile phone tracking tools previously.
They are also collecting location data transmitted by mobile apps. An NSA program, code-named HAPPYFOOT, helps the NSA to map Internet addresses to physical locations more precisely than is possible with traditional Internet geolocation services.
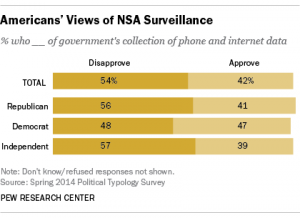 How do Americans feel?
How do Americans feel?
PEW research shows what Americans think about online privacy and the NSA.
Overall, 54% of Americans disapprove of the US Government collecting telephone and Internet data for anti-terrorism efforts.
74% said they should not give up their privacy and freedom for the sake of safety.
93% think it is important to control who can get their information.
38% think they have only some control over their own information.
Cyber Legislation
CISPA had alarmed the privacy community by giving companies the ability to share cyber security information with federal agencies, including the NSA, “notwithstanding any other provision of law.” That means CISPA’s information-sharing channel, created for responding quickly to hacks and breaches, could also provide a loophole in privacy laws that would enable warrant-less intelligence and surveillance. The information they gather, including all hacked data and any incidental information swept up in the process, would be added to a massive database. The FBI, CIA, and NSA would then be free to query this data at their leisure.
This is how CISPA would create a huge expansion of the “backdoor” search capabilities that the government uses to skirt the 4th Amendment and spy on Internet users without warrants and with virtually no oversight.
How to prevent being spied on by the NSA and other data collectors without going off the grid
It may be impossible to completely prevent the NSA from spying on you, but you can try and make it much harder.
- Avoid popular Online Consumer services – These include Google, Facebook, and DropBox.
- An alternative to DropBox is SpiderOak.
- A common alternatives to Google is DuckDuckGo.
- Mashable has published a list of private social networks to help you avoid the Facebook plague.
 Encrypt your hard drive – You may have password protection on your files but you should go a whole step further and encrypt the entire hard drive.
Encrypt your hard drive – You may have password protection on your files but you should go a whole step further and encrypt the entire hard drive.
- Avoid online tracking – On you browser you can use the do-not-track setting but you can go a step farther and use a plugin to stop tracking. Some reputable plugins for this include:
- Encrypt your email and chat messages – Encrypt your messages before you send them. Some common email clients with encryption include:
- Microsoft Outlook – This has encyption options if you want to use them.
- Runbox (a Norwegian secure email client) – Claims to be unreachable by the NSA.
- HushMail – Not as popular but is completely encypted.
If you chat on the Internet, you can encypt those messages too.
- ChatCrypt – Encrypts the message when it sends and can only be read by the end user, also known as end-to-end encryption.
If you use common instant messaging through Google, AOL, Yahoo or Microsoft you can use a chat extension called OTR (Off the record) which enables end-to-end encryption.
- Use TOR for online browsing – TOR stands for The Onion Router. Like an onion, it layers multiple levels of security. Basically, it bounces communication around a network of relays which makes it very difficult to track.
 Many browsers also have a private mode.
Many browsers also have a private mode.
- Firefox – Private Browsing
- Chrome – Incognito mode
- Internet Explorer – InPrivate feature
Online Privacy in Europe
A recent draft of the British Investigatory Powers Bill will require companies to store information for up to a year. Communications companies would hold details of which websites and apps a person uses.
 Recently, the European Union has decided to invalidate the current voluntary safe harbor because they believe the US cannot adequately protect its privacy. There have been reports that European companies are transferring data out of US territory for safe keeping.
Recently, the European Union has decided to invalidate the current voluntary safe harbor because they believe the US cannot adequately protect its privacy. There have been reports that European companies are transferring data out of US territory for safe keeping.
EU-US Privacy Shield
The US Government released full text of the new European Union-US Privacy Shield on Feb 29. This is not yet law.
Citizen complaints – The new agreement gives companies and citizens the chance to complain and dispute any mishandling of records and personal information.
Targeted spying – This will now be limited to: detect and counter threats from espionage, terrorism, weapons of mass destruction, threats to the armed forces, or transnational criminal threats.
The proposed framework includes the following features:
- Companies must provide greater transparency with respect to their data collection, use, and sharing practices through more robust and detailed privacy policies
- If a company handles human resource (employee) data, it must agree to cooperate and comply with EU Data Protection Authorities (DPAs)
- Companies transferring personal data to third-party service providers remain fully responsible for the proper handling of personal data; must conduct appropriate due diligence concerning its service provider; and must properly monitor and re-mediate any deficiencies of its service providers relating to the handling of personal data
Our Advice
Ideally, companies should give consumers control over the information they divulge. This becomes even more urgent since corporations so freely share information with government authorities. Until consumers begin reading those 30-page privacy policies rather than blindly accepting them, they will continue falling for the same traps. Generally, as consumers we must understand that the “free” services we consume are actually very expensive. It often comes at the price of our privacy. So take a long hard look at the next privacy policy you’re asked to accept. You may be better served just paying cash instead.
Social Media Copyright Issues: Fair Use or Infringement?
Social media copyright issues have become a hot topic in recent months. Nearly everyone has shared something on social media that was copyrighted by someone else. But what is fair to use on social media and what infringes on the rights of the copyright holder?
Is it fair use or infringement?
If you do not get a license from the copyright holder then the only way to use the content is through something called “fair use”.
What is fair use?
Generally, fair use covers any copyrighted material that was shared with a “transformative” purpose. This might constitute a comment, criticism, or parody accompanying material. Such sharing can take place without permission from the copyright owner.
Categories of Fair Use
- Commentary and Criticism – Commenting upon or critiquing copyrighted material. Examples include online reviews, news reports, education courses, or court case.
- Parody – A parody takes copyrighted material and ridicules it in a comedic way.
Fair Use Checklist
Not sure if you’re allowed to share something under “fair use”? Run it through this checklist to be sure before you post.
☐ Purpose and Nature of Use
The use of copyrighted material must be “transformative”. This means you took the time to add new meaning or value to the copyrighted material with new information, aesthetics, insights, or understandings.
Example of Fair Use: Google images – All Google images are copyrighted by the owner. Google’s use is considered “transformative” because it displays pictures in a different way, for a new purpose.
Example of Fair Use: Scary Movie Series – This movie series is a parody which borrows copyrighted material in order to ridicule it. Producers added value using new information, aesthetics, insights, and understandings.
Example of Infringement: Posting a copyrighted image on social media is for aesthetic or entertainment purposes. This is likely NOT a different use than the copyright holder intended and does not transform the work.
☐ Nature of the Work
Using copyrighted information has more leeway in fair use than copyrighted creative works. Also, there is more leeway in using published work rather than unpublished work.
☐ Amount and Substantiality of the Portion Used
Less is more. Meaning the less you use of the copyrighted material the more likely it will be considered fair use.
Exception: Using the most memorable (although small) part of a copyrighted work, such as the opening riff of “Sweet Child O’ Mine” by Guns N’ Roses.
Exception: Parodies – Quite a bit of a copyrighted material, even the heart of the material, can be used for parody. The Supreme Court acknowledges that “the heart is also what most readily conjures up the [original] for parody, and it is the heart at which parody takes aim,” as decided in Campbell v. Acuff-Rose Music,510 U.S. 569 (1994)
☐ Effect of Use Upon Market or Value
If you deprive the copyright holder income or undermine copyrighted work that could have potential market it is not fair use and you are most likely looking at a lawsuit. This holds true even if you are not using the copyrighted work directly.
Example of Infringement: An artist used a copyrighted photo to produce wood sculptures and earned a lot of money selling them. Even though the photographer did not plan on make sculptures it was considered a potential market and the court ruled in favor of the photographer.
[alertbox color=”blue”]MYTH
If you list a source, using copyrighted material is permissible.[/alertbox]
This is probably the most popular myth about copyrighted material. Even if you list your source, using copyrighted work without permission is still an infringement, especially if you are making income from it.
☐ Check Original Source
Sometimes the original source will have copyright notices. If you are unsure, be safe and obtain a license from the copyright holder.
 ☐ Check Social Media Terms and Conditions
☐ Check Social Media Terms and Conditions
When someone posts original work on social media, you should check the authorization to re-post, re-tweet, or re-pin that content. Read our blog article Social Media Content Rights for more detail.
Example: Pinterest’s term of service states that if a user posts content on Pinterest they are providing a license to all other users to use that content on Pinterest.
☐ Post a link instead of content
On social media, post a link to the original source of the material instead of the material itself. While this is still infringement, the chances of a complaint are much lower (especially since everyone does it). This does support a fair use defense.
☐ Keep Sharing Within Network
When you find content on social media you want to share, keep it within that network. Always read the terms and services before sharing.
[alertbox color=”blue”]
MYTH
Content posted on social media is fair game.
[/alertbox]
Some may think that if the content is on social media then it is fair game to use. This is not the case – the copyright still belongs to the copyright holder.
 You can be held at fault for posting copyrighted material or even sharing something someone else posted that was copyrighted. This seems to happen so frequently on social media that the chances of litigation are low, but it’s still a risk.
You can be held at fault for posting copyrighted material or even sharing something someone else posted that was copyrighted. This seems to happen so frequently on social media that the chances of litigation are low, but it’s still a risk.
U.S. Copyright Office Fair Use contains comprehensive information if you’d like additional information.







