EMV Chip and PIN Credit Cards
EMV Chip and PIN Credit Cards
You may be receiving new credit cards this summer: the chip and PIN credit cards.
Credit card terminals must be upgraded to the new technology, common in Europe, by October 1st
or will be held liable for Credit Card fraud that happens in their establishment.
The EMV chip and pin cards reduce credit card data theft by containing a chip that encodes data transferred to the merchant. They are also tougher to clone than
magnetic strips.
Reducing, But Not Eliminating, Data Theft
This technology will not do away entirely with data theft. Online fraud and insecure websites that might store your data are not protected by the chip. For that, you need complicated, hard to guess passwords. And since credit card fraud still happens overseas, the system is not fail-safe.
For businesses and companies, this means it is their responsibility to upgrade credit card terminals for the new technology or they will be held liable for credit card fraud.
My Computer Files are Being Held for Ransom!
 Ransomware
Ransomware
Ransomware, often going by the specific name CryptoLocker or Cryptowall, is a form of malware that, when installed on your computer, encrypts your files and locks them with a key. It then demands a ransom in digital currency within a set amount of time, or the key will be deleted and the files will be inaccessible.
How do you get it Ransomware?
The most common way to become infected with ransomware is to download it inadvertently. When downloaded, the malware sets to work.
Ransomware is often installed by:
- Opening email attachments
- Clicking on banner ads
Why doesn’t my antivirus protection catch Ransomware?
Generally speaking, Ransomware is sneaky malware that slips in to your computer because you have inadvertently installed it. You’ve gone ahead and told your computer to install things, and the malware takes advantage.
[pullquote cite=”- George W.”]”I got an alarmed call from my grandma. She likes playing online games, and clicked on an ad promising her more coins for her game, and moments later she had a message across her screen telling her that her computer had been infected, and that she had to call a number and pay to get the problem resolved. Fortunately, my grandma didn’t have many files on her computer. We wiped the hard drive and reinstalled Windows. But if she’d had important paperwork or photos without any backups, she would have been in a lot of trouble.”[/pullquote][space10]
Who is the biggest target?
This malware can attack anyone, but it causes the most damage to businesses, as they have more valuable data that is not easily replaced. Ransomware is designed to get money by holding your data for ransom.
How do I avoid Ransomware?
Don’t click on things you shouldn’t, or open unexpected files. Functionally we all know this isn’t always the case, however, and sometimes files slip through because they are deceptive.
If you become infected with Ransomware:
- Have secondary backups of important files that are not updated real time, this way, if you need to roll back, you have something unattached that is not infected.
- Unhook your computer from the internet RIGHT AWAY. All files may not have a chance to be encrypted.
[alertbox color=”red” icon=”delete” hide=”0″]
A few companies claim to be able to undo the damage, or have released the keys to unlock encrypted data, but this has not been guaranteed to work in all cases, especially since criminals update the software all the time.
[/alertbox] [space5]
My files are being held for ransom!
If you do find that you have this software, you have two options:
- Pay up and hope the keys they supply you to unlock your data works as indicated. This is risky as it encourages criminals to continue the scam, and since they ARE untrusted people, nothing is guaranteed.
- Wipe computer clean and restore from backup.
Hacking and computer exploits have become more sophisticated and with more businesses online, the risk is real. Precautions and backups are the most surefire way to avoid the worst of damage from hackers, criminals and emergencies when your files are being held for ransom. For more information on internet security, visit our blog at Appletree Mediaworks, LLC.
For more information visit:
– http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6657-ransomware-cryptolocker-protection.html
– https://www.foolishit.com/cryptoprevent-malware-prevention/
– http://www.welivesecurity.com/2013/12/12/11-things-you-can-do-to-protect-against-ransomware-including-cryptolocker/
– https://blog.malwarebytes.org/intelligence/2013/10/cryptolocker-ransomware-what-you-need-to-know/
Masque Attack
 Masque Attack was a recent vulnerability involving Apple’s mobile operating system that would allow hackers to use web pages, text messages, and emails to trick people into downloading fake apps that disclose personal information.
Masque Attack was a recent vulnerability involving Apple’s mobile operating system that would allow hackers to use web pages, text messages, and emails to trick people into downloading fake apps that disclose personal information.
The concern is that fake apps resembling real apps such as banks or email program could replace genuine apps installed through the App Store, and siphon personal data without user knowledge. Obviously there is a potential for a sneaky vulnerability on any device, but it’s noteworthy for Apple, which many of its users consider more resistant to hacks and problems.
There is no evidence the vulnerability is being used in the US, but the bug affects iOS 7 or later. 95 percent of Apple mobile devices could be vulnerable.
Apple issued a statement about the matter, that it does not know of any customers who were affected by the issue, and to only download apps from trusted sources.
How To Avoid This, whether you use an iPhone, or an Android or Windows device:
- Don’t install apps from third party sources. Only use Apple’s App store (or the appropriate one to your device) or your own organization if it has apps.
- Don’t click ‘install’ from a popup, even if the popup seems legitimate.
- If iOS says “Untrusted App Developer” click on “Don’t Trust” and uninstall the app.
Websites and the CryptoPHP Infection
 Could Your Site Be Infected?
Could Your Site Be Infected?
If your website uses a content management system such as WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal, you will want to be aware of the CryptoPHP infection. Like many infections of this nature, the CryptoPHP infection is both sneaky, and can spread the maliciousness once it’s there, so it’s good to be aware of it if you may have the potential to encounter it.
So Just What Is it?
CryptoPHP is an infection that works like a botnet. It is a sophisticated program that uses your website to conduct illegal “black-hat” SEO tactics such as adding links to other, possibly malicious websites. It can also upgrade itself, and since it communicates with other servers it can update itself and behave as a drone that could do anything from sending spam to attacking other sites.
How Do You Get it?
CryptoPHP is acquired by downloading and installing a theme to their WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal site – specifically a free theme found online. The infected theme has a nulled script that contains a line of code that appears to include PHP but instead appears to call on an image. Hidden inside the image is the real, malicious code.
How Can I Prevent It?
There are a few simple ways to avoid infection:
- Don’t use free downloaded themes on your site – it is difficult to tell what is infected and what is not.
- Don’t accumulate extra “unused” themes just sitting around on your site. It’s easy to collect dozens of these while trying them out, but best to reduce this number as much as possible. Your current theme and ones in development are all you really need.
- The sites we here at Appletree Mediaworks LLC create are CryptoPHP-free.
How To Know If You’re Infected
For WordPress: Install the Wordfence plugin and enable the option to scan images – CryptoPHP hides in a png image, but is actually obfuscated code. This will detect the infection.
Other sites: Download all source code and search for this line:
<?php include(‘assets/images/social.png’); ?>
Our sites here at Appletree MediaWorks LLC are CryptoPHP-free. If you have concerns over your own sites, or have any questions on keeping your website up to date and secure, contact us or visit our blog for more information.
—
For More Information on CryptoPHP – http://www.wordfence.com/blog/2014/11/wordpress-security-nulled-scripts-cryptophp-infection/
How to Avoid Getting Your Email Hacked
How Do You Avoid Getting Your Email Hacked?
- Duplicating usernames and passwords is risky. If you use the same username or password on several different websites, only one of those sites being compromised can make all of your accounts vulnerable. Many hackers use brute force or dictionary attacks in which a program is set up to attempt countless password combinations rapidly. The simpler your password, the easier it will be to “guess” by the program.
- Suggestions: Set up unique login credentials on each website or service you use, making sure to create complex passwords. To remember all of them, use a program or service such as 1Password, LastPass, or KeePass to help manage and keep track of your information. Once you’re set up with a password manager, creating 40-character passwords (and never forgetting them) becomes a breeze!
- Keep your software up to date. Out of date software is risky, especially when it comes to web browsers, browser plugins, and other web-based software. Make sure to keep your operating system and antivirus software up to date. Run anti-spyware programs regularly.
- Suggestions: Many programs update automatically. Still, it is a good idea to set your phone or calendar to remind you to check on these things every few weeks.
- Pay Attention to Login Sessions. Make sure that you are the only person logging into your accounts. You can often monitor recent activity with popular online services such as Facebook and Gmail.
- Suggestions: Change your passwords if things seem fishy. Do not create obvious security questions that people can find the answers to simply by searching Facebook or other sites.
- Think Before You Click! If you receive an ambiguous or unexpected email asking you to click a link, even if it appears to come from a relative or close friend – don’t do it. Contact the person over the phone and ask whether or not they actually sent it. The same goes for attachments.
- Suggestions: Ignore and delete emails like this, even if they appear to come from friends, family, or banks. Don’t click the link or open the attachment – it’s a surefire way to get your info stolen.
- Watch where you log in from. Be careful if you are logging in from a public computer or a network that is not secure. Be sure to log out of any services you used and clear the browser’s cache before walking away from any public computer.
- If Two-Step Authentication is an option, use it! Two-step authentication often requires an extra step, such as inputting a code you are texted, particularly on a new machine. If your email service has this feature, it may very well be worth the effort.
Know that none of this is absolutely foolproof as identity theft and account hacking becomes more rampant. It is best to set up your accounts so that if one gets compromised, the rest remain secure. Have a plan set up for what to do if an email gets hacked or a credit card gets stolen. Keep in mind that this is an extremely common, if problematic.
If your account gets hacked:
- Scan your computer for viruses, malware, and keystroke loggers. It is important to do this first before changing passwords, or the same problem could occur again if your computer itself has been compromised.
- Change your passwords and security questions if you can still access your account.
- If you cannot access your account, follow the directions in the site’s help center – most sites have guides about what to do.
- Report the incident. You may get access to identity protection services through the site.
- Let people know you got hacked and not to click any links appearing to come from you until the problem has been sorted out.
Scams: Energy Bill Service Scam
Lets Have A Look At An Energy Bill Service Scam
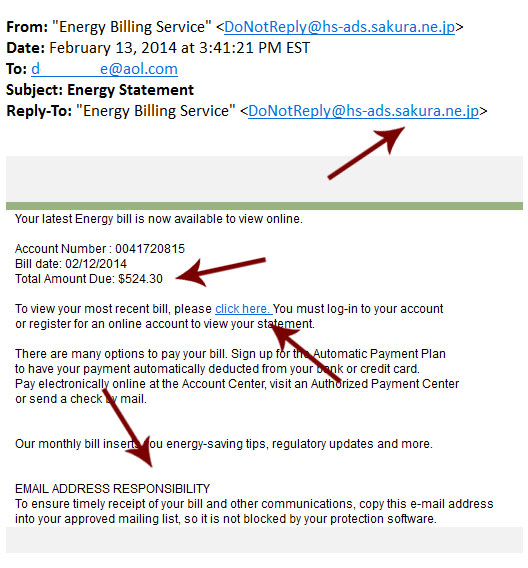
Here we have a classic scam email captured in its natural environment, which presents a good opportunity to learn how to spot them. This one is rather straightforward and deceptive. Note the alarming nature of the email, intent on distracting attention away from the fact that your “energy bill” is being sent from Japan. It is worth noting that email addresses are notoriously easy to spoof, so it won’t always be so obvious. Scam emails can just as easily appear as if they came from a legitimate source.
A better tell might be the obligatory “click here” link. If you hover over it with your mouse, the link itself is suspicious – the URL has nothing to do with an energy company. Link targets are much more difficult to fake, but can sometimes look very similar to a more legitimate address, so look closely!
This scammer even has the nerve to instruct you to add their email address to your approved mailing list so that future scams won’t be blocked by your spam filter. It is never a good idea to do this unless you are 100% certain the email is legit.
As always, if you receive an email like this, do not immediately click on the link. Instead, open up your web browser separately and navigate to your actual utilities company’s website if you are concerned. Delete the email and go about your normal business.
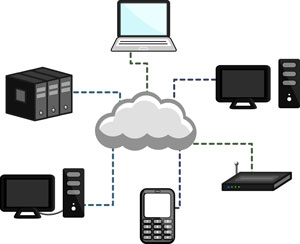
The Good and the Bad of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing seems inescapable. Phones and devices have cloud servers for files, any user can get free cloud backups for their own computers, and even federal and state governments are investing in cloud computing for their own data. But just what is it, and is it safe?
What Is It?
First, we had computers that had hard drives with information and programs on them, and then we used discs to move that information from computer to the next. These discs were small, so we took to thumb drives, but this was problematic if you forgot your thumb drive at home or work or school. Those of us who had web mail account like Yahoo or Hotmail recognized we could just email ourselves the data, and open it from wherever.
This was the early stage of Cloud Computing.
Cloud computing is the practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the internet to store and manage data, rather than a local server, or a personal computer. Given that few of us stick to just one computer these days –between home, work, school, laptops, tablets, and other devices – having ready access to that information on any device is important. This is where cloud computing comes in.
Where is it stored?
Cloud computing is named as such because information or even programs are used or run from a number of application or storage servers kept and backed up off site, and accessed through multiple computers where the user logs into an interface for access. A simple example of this is web-based email which is accessible through a web browser and website, but available through any computer.
Individuals and companies often resort to third-party cloud storage, such as iCloud, Dropbox, Google Drive and others. Companies may wish to back up not only files, but whole computers, databases, or programs for use.
When are people going to use this tech?
This sort of technology has been used since the ‘90s when people backed up files on web hosts or used web-based email clients. With the ever increasing use of mobile computing, cloud hosting has become more prevalent and will continue to do so for the foreseeable future.
Why is this needed?
The more mobile people become with their computing, the more important it will be to have access to files, data, and programs remotely. While devices and computers have ever-increasingly large hard drives and can hold more info, hauling around secondary drives and copying information over is redundant and unnecessary.
For companies and industries, a base location for all information is valuable in the interests of saving money and time. Instead of a slowly depreciating server under a desk or stuck in the back room, all information is available and reliably backed up offsite. This also allows for people in multiple locations, branches, or buildings, to have access to and immediately update information as needed.
What are the potential pitfalls and drawbacks?
Cloud computing has some very real drawbacks and concerns, and some of them do not have good solutions at this time:
- Access: To access the cloud (whatever form of cloud you are accessing at the moment), the user needs internet access. Without wifi or otherwise, access to files and software severely limits what can be done. This is becoming less and less a problem as time goes on, but still could come up as an issue.
- Security: Every day the news broadcasts another company or institution getting hacked. And as security gets more sophisticated, hackers always seem one step ahead. Information could be accessed and stolen during a number of points in the cloud computing process, whether it be a hacker discovering a means of getting in, or a user with a weak password.
- Privacy: Housing your data somewhere on the web inevitably means someone else may have access to it. Along with the aforementioned hackers, NSA access to various servers and databases has been argued and discussed extensively throughout the last year. While a company may not have anything to hide, they may not want that data accessible in general.
- Third Party Control: Ultimately, in handing over data and programs to a third party, a company or institution is handing the keys over to someone else. Not everyone likes this or feels comfortable with it, and would prefer to have complete control over their information.
Despite the potential hazards of cloud computing, large companies and even government and official institutions more and more are turning in that direction due to reduced costs and ease of use. The debate and concern over the security of private information will only increase as hackers are more sophisticated and computing becomes more ubiquitous. But cloud computing is not going away any time soon.
For more information on cloud computing and internet security in general, follow the Appletree Media blog.
More On Cloud Computing:
http://computer.howstuffworks.com/cloud-computing/cloud-computing.htm
http://www.moneycrashers.com/cloud-computing-basics/
http://www.thefiscaltimes.com/2014/10/14/States-Turn-Cloud-Computing-Cost-Savings
http://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/default/files/omb/assets/egov_docs/25-point-implementation-plan-to-reform-federal-it.pdf
http://www.itproportal.com/2014/10/13/whitepaper-five-myths-cloud-computing/
Union Edge Tech Tips – October 29, 2014
Verizon’s Cookies and Windows XP Hackers
Verizon’s ‘Perma-Cookie’ Is a Privacy-Killing Machine
Apparently Verizon tracks your internet use and there is no way to opt out of it.
When surfing the internet using Verizon’s internet, a string of about 50 characters is added to the end of every URL you go to. Verizon calls this a Unique Identifier Header (UIDH), its essentially a serial number that advertisers can use to identify you on the web when you use Verizon’s internet service.
According to Verizon spokeswoman Debra Lewis, there’s no way to turn it off. She says that Verizon doesn’t use the UIDH to create customer profiles, and if you opt out of the company’s Relevant Mobile Advertising program by logging into your Verizon account. Then Verizon and its advertising partners won’t be using it to create targeted ads.
Because Verizon is broadcasting this unique identifier to every website, ad networks could start using it to build a profile of your web activity, even if you’ve opted out and without your consent.
There’s rumor that AT&T and T-mobile are doing the same thing to their users. To see what is being captured by Verizon or AT&T, Click Here to check your mobile device.
Full Article Text: WIRED -Verizon’s “Perma-Cookie”
Windows XP Is Still a Favorite Among Hackers
As much as people love Windows XP, there are reasons to upgrade to something newer. Almost 25% of all PCs are still running Windows XP, that’s 1.5 billion computers.
Back in April, Microsoft stopped supporting and updating XP. Leaving XP users open to new exploits. Researchers have found that close to ½ million US computers are hacked, and are botnets that send back information such as passwords and banking information.
This is only going to get worse, if you’re still running XP its time to think about upgrading your Malware software or updating to Windows 7 or soon 9.
Further Reading: MIT Technology Review – Windows XP Is Still A Favorite Among Hackers
Social Media Tips for Unions:
- It can’t hurt to have different social media platforms linked together even if they have similar info. People should be able to get from one platform to website to another platform with relative ease.
- It is a good idea to have the basic info filled out on any given platform because you never know which one people are going to go to first, even if you don’t intend to update regularly.
- Good to consider the following social media platforms:
- Facebook – A given. People use this extensively and refer to it frequently to keep track of current events and information.
- Twitter – Twitter is great for on-the-spot rapid posts and updates of current events as they happen.
- G+ – Set up G+ so people local to the area can find information on a given Local, and the information links up with the map feature. Google might put this information in the sidebar on the search page when someone does a search so that it displays more prominently.
- Pinterest – Pinterest is a great way to spread around images of events and things going on – photos are the way to go with this platform, and if you use them extensively, you’ll want to be sure to post them here.
- Ello – Ello is brand-new and still in beta, but they promise not to sell your information for advertising. It might be the right way to go, and could send the right image.
- Your own Website – Be sure you hook everything to the website and back again. Think of your website and social media platforms as a network that ties together. Better to get the word out when you need to!
Always practice Safe Tech!!
Read More About Crafting Strong Passwords at the Appletree Media Blog.
Cat Tech Tips – Computer Updates

Cat Tech Tips – Computer Updates
You’re merrily typing along or browsing Facebook when suddenly Windows informs you that it has updated and wants to restart – what’s that all about? If Windows needs to update this often, what ELSE needs to be updated?
The answer is: Quite a few things! And many of those things have probably gone without computer updates for years. Keeping your machine updated makes it run more smoothly, and keeps it more secure.
So what needs to be updated?
– Windows Updates: Windows usually updates periodically on its own, but it doesn’t hurt to check and see what non-essential updates need to be installed, and to just tell everything to get it over with right now.
– Antivirus Updates: Your antivirus software should be updating and scanning regularly on its own if it was installed properly, but it doesn’t hurt to check.
– Driver Updates: Drivers are little programs that make your hardware play nice with the rest of the computer, and you rarely think to update them. Software like Device Doctor can get everything up to where it should be. Be sure to back up your computer first!
– Browser Updates: Browser updates patch security holes and are essential – check to make sure your updates are turned on and if not, update those browsers manually.
– Third Party Updates: Other programs like Flash, Java, and Adobe Reader will prompt you to update. They will nag, badger and annoy you with reminders, often times they will badger you to the point your antivirus program will question their motives. We may never know why a PDF reader needs more updates than everything else combined, but just let it do its thing.*
*IMPORTANT: Do read the text on what you are updating. Sometimes sneaky malware will masquerade as something legitimate, and sometimes McAfee will try to slip in with other programs such as taskbars. Uncheck those checkboxes if you don’t want a certain piece of software.
Proceed With Caution
As always, back up your computer or tablet before making major changes (such as the driver updates), and we are not responsible for any issues you may encounter, such as throwing computer out the window in frustration after finding McAfee sneaking in for the sixth time.
iCloud Hack and Compromising Data
Take a photo – it will last longer. But do you really want it to?
By now practically everyone has heard about the hacker that managed to acquire private, compromising celebrity photos and post them to distribute on websites. While all the details are still being worked out, the most common theory is that the hacker managed to get to these photos through the use of brute force software and an exploit or hack in iCloud, Apple’s iPhone cloud service.
This particular episode in questionable internet security is making news because of the enraged celebrity targets and the wildfire pace at which the images are making their rounds, but this sort of data breach could happen to anyone. And until Apple and investigators figure out and announce just what happened, users are left trying to keep things secure as possible.
What can you do to keep your data secure?
Strong Passwords
Email is inherently unsecure. Do you really need a backup of all of your emails sent up to a vulnerable cloud too? It’s likely your work email is backed up by your employer and usually personal email providers backup their own email servers, so don’t allow your email to be copied to a cloud too. If you truly need an important email for reference later? Go old school: print it out and store it in a safe or forward it to an encrypted email server for storage.
Photo Stream
Cloud storage is not inherently the most secure way to keep data, and it’s also known as a potential target for hackers. Incidentally, if you have an Apple phone or tablet, Photo Stream may be active and you might not even know it.
You can disable the Photo Stream by doing the following: Go to “Settings,” then “Storage & Backup” and stop the “Photo Stream” feature. This will stop all your photos from automatically uploading to the cloud.
Android and other phones have their own means of cloud backups to check into as well. Some require setting up manually, and others may prompt you to activate them. Read the messages you are given, and check into your settings from time to time.
2-Step Verification
Although it may not have helped in the case of the iCloud hack, 2-Step Verification increases security in devices, and many services including Apple, Twitter, and Gmail have it. 2-Step verification requires that after the user enters a password, you go through an additional step of verification (such as entering a code you are texted) on new devices.
Precautions
Without blaming the victim, keeping compromising photos off easily accessible devices warrants mentioning as well. While phones make it easy to take and send a quick snapshot, this is not inherently secure. And on the user-end, even if your own tech is secure remember that any photo you send to someone else could end up on the wilds of the internet.
If you want to take those potentially compromising photos? A camera may be a better option.