Social Media After Death
 As of this year, at least 2.34 billion people worldwide are social media users. In the United States alone, 79% of people have a social media profile. Something we don’t really think about when signing up for these accounts is what will happen to them when we pass away. Should we write your passwords down somewhere? Can someone gain access to them after we’re gone? What happens to your social media after death? It is reported that around 8,000 Facebook users die every day. It’s important that policies and protocols are put into place.
As of this year, at least 2.34 billion people worldwide are social media users. In the United States alone, 79% of people have a social media profile. Something we don’t really think about when signing up for these accounts is what will happen to them when we pass away. Should we write your passwords down somewhere? Can someone gain access to them after we’re gone? What happens to your social media after death? It is reported that around 8,000 Facebook users die every day. It’s important that policies and protocols are put into place.
Facebook & Instagram
Facebook and Instagram are the only major social media platforms that “memorialize” your account.
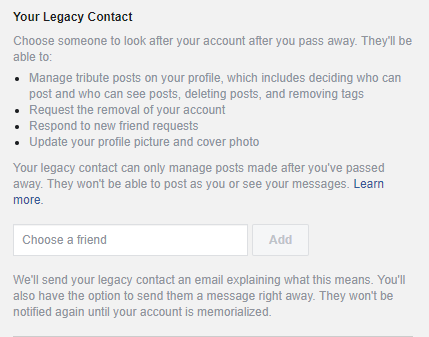
With Facebook, you can set up a “legacy contact”. This is the person who will manage your account after you’re gone. To set up your legacy contact, go into your Facebook general settings and select Manage Account and choose the person to take this role. As seen in this screenshot, the person you choose to be your legacy contact will not be able to post as you or read your messages. If you don’t want to have a legacy contact, you can also request for your account to be deleted when the time comes. To request for an account to be memorialized, contact Facebook here.
Instagram does things a little bit different. There is no legacy contact that can manage your account for you when you die. Once a family or friend sends a report and the account is memorialized, it appears mostly the same. However, the account will not show up as a recommendation anywhere on the app (such as in the explore section). Nothing can be deleted or changed on the account after it is memorialized.
Other Platforms
For most other social media platforms (including Twitter), there are no memorialized profiles, therefore a family member has to request the removal of a deceased user’s account. In general, social media platforms will never give login details to anyone but the account owner, even immediate family members. This would violate most terms of service. If you want someone to have full access to your social media, it may be smart for you to put this in writing with something like a digital will. This will hand over ownership of your accounts after you pass away. This helps avoid violating any terms of service.
Computers and Devices
That great password you’ve set up on your computer or device to keep others out will do just that after your death. As a rule, device manufacturers will not grant access to others to get around your pass codes and passwords. Keep in mind many of your online accounts also have 2-factor authentication too. Banks and other service providers are happy to work with whoever holds your power of attorney posthumously, but email accounts and other online accounts will need to be accessed with the information you leave in your digital will.
Though it may be odd, it is important to have a plan for what happens to your social media and online accounts after death. Set up your legacy contact on Facebook today. Also, inform your friends and family by sharing this with them! Subscribe to our bi-weekly e-newsletter for more helpful information like this!
Social Media Content Rights
 Who Owns Rights To Your Social Media Content?
Who Owns Rights To Your Social Media Content?
Occasionally we see those posts on Facebook where a user declares that they don’t have to abide by Facebook’s terms of service, having written a clause in a post. We all know this is a hoax. After all, you already agreed to their terms by making an account.
Even so, what is the nature of your media on someone else’s social media network? What are your social media content rights? It varies, and it’s murky.
Facebook:
 Facebook’s terms are broad. Since their (and your) materials are hosted on various servers, their terms are written so that the data can be shared as desired or needed by them. According to Scoopshot, this does not end when you delete your account either. Your images may be hosted on one of their servers elsewhere.
Facebook’s terms are broad. Since their (and your) materials are hosted on various servers, their terms are written so that the data can be shared as desired or needed by them. According to Scoopshot, this does not end when you delete your account either. Your images may be hosted on one of their servers elsewhere.
Facebook says they have no intention of using these images for their own purposes, selling them, or otherwise distributing them. However, their legal terms are written so that they can.
Read Facebook’s Terms of Service
Don’t like it? Don’t host or post your media there.
Twitter:
 Media you post on Twitter stays yours, says Twitter, but their terms specify that they can distribute the materials posted through them. Again, their terms are open-ended.
Media you post on Twitter stays yours, says Twitter, but their terms specify that they can distribute the materials posted through them. Again, their terms are open-ended.
Twitter’s Terms of Service state “By submitting, posting or displaying Content on or through the Services, you grant us a worldwide, non-exclusive, royalty-free license (with the right to sublicense) to use, copy, reproduce, process, adapt, modify, publish, transmit, display and distribute such Content in any and all media or distribution methods (now known or later developed).”
Instagram:
 Your material belongs to you on Instagram, with the usual warnings about network sharing. They can display those images as they see fit. You are also responsible for not hosting copyright materials belonging to someone else.
Your material belongs to you on Instagram, with the usual warnings about network sharing. They can display those images as they see fit. You are also responsible for not hosting copyright materials belonging to someone else.
The terms of service for Instagram state “you hereby grant to Instagram a non-exclusive, fully paid and royalty-free, transferable, sub-licensable, worldwide license to use the Content that you post on or through the Service, subject to the Service’s Privacy Policy, available here including but not limited to Sections 3 (“Sharing of Your Information”), 4 (“How We Store Your Information”), and 5 (“Your Choices About Your Information”).”
Flickr:
 Flickr is owned by Yahoo, and there has been a lot of fuss over who owns those images. Currently, Flickr claims that you own the rights to your images in their social media network.
Flickr is owned by Yahoo, and there has been a lot of fuss over who owns those images. Currently, Flickr claims that you own the rights to your images in their social media network.
Other social media networks state that you own your media with the usual server/host limitations. They also assume that you are acknowledging that you own the materials you upload.
Ultimately, social media networks are going to cover all their bases for the foreseeable future, and make sure they are covered legally. This generally means they will broadly define their own rights. The result may be that they are allowed rights to your media. Your option, then, is to think carefully about where you are posting your media.




